Mapon fleet management platform provides valuable insights into various aspects of vehicle operations, including fuel consumption. However, it's important to recognize that there may be differences between the fuel-up data recorded on the platform and the actual refueling at a petrol station. This article delves into the factors contributing to these discrepancies.
CAN Fuel Data: Precision and Limitations
CAN data is obtained directly from a vehicle's onboard diagnostics system. It provides information on various aspects of a vehicle's performance, including fuel consumption. However, it's important to note that CAN fuel data precision is typically around 80%. This indicates that while it provides valuable insights, it may not consistently offer pinpoint accuracy.
Factors Affecting CAN Data Precision:
-
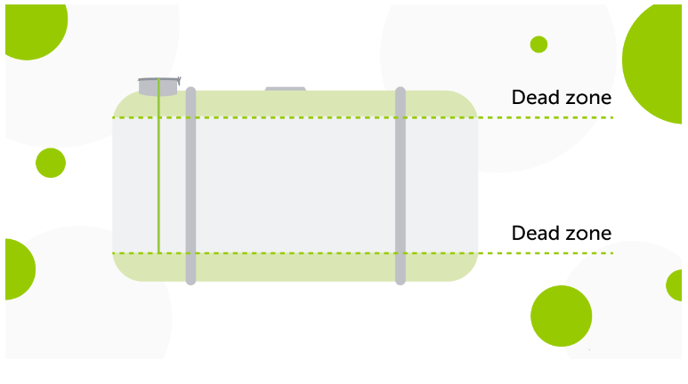
Technical specifics: CAN fuel-up readings rely on a built-in fuel level sensor of the vehicle, meaning that the sensor does not account for the dead zones that exist in the upper and lower parts of the fuel tank. These dead zones can represent a significant portion of the tank's volume, potentially up to 10%.
-
Vehicle Age and Condition: Older vehicles may have less precise CAN data due to potential sensor wear and tear. Additionally, the accuracy of CAN data can be affected by the condition of the vehicle's components.
-
Sensor Calibration: The accuracy of CAN data depends on the calibration and accuracy of the vehicle's sensors. Any discrepancies in sensor readings can lead to variations in reported fuel consumption.
Fuel Sensor Data: Precision and Limitations
A fuel level sensor is a high-capacity sensor that measures the fuel level and its changes in the tank (refills and drainages). Fuel level sensors are known for being more precise than other fuel consumption tracking devices. If the sensor is correctly installed, its error will only be from 1-2%.
Factors Affecting Fuel Sensor Data Precision:
- Sensor Calibration: Fuel level sensor calibration involves setting up or adjusting the sensor to accurately measure the fuel level in a vehicle's tank. Some sensors may experience a natural drift in their calibration over time, even in stable conditions, therefore recalibration of the tank is recommended once every couple of years.
- Contamination and buildup: Dust, debris, or other contaminants can accumulate on sensors and in the fuel tank, affecting their performance and calibration.
- Mechanical or Electrical Interference: Physical damage to the sensor, for example at the connection point, can disrupt the sensor's operation.
- Sensor Wear and Tear: Over time, sensors may experience wear and tear, which can alter their accuracy.
- Count of Fuel Tanks: Dual-tank vehicles often have mechanisms for switching between tanks. These mechanisms can introduce potential points of failure or errors in sensor readings due to technical specifications.
Discrepancies with Actual Fueling Data
Actual fueling data, obtained from gas stations, represents the physical amount of fuel added to the vehicle's tank. This data is highly accurate. However, it may not align with CAN data due to several reasons:
- Tank Shape and Type of Machinery - The shape and type of a vehicle's fuel tank can impact how it is filled. Irregularly shaped tanks or tanks with unique designs may lead to variations in fuel-up measurements.
- Type of Fuel Used (Summer vs. Winter) - The type of fuel used can vary depending on the season. Summer blends of fuel may have different energy content compared to winter blends. This discrepancy can affect fuel up and consumption measurements.
- Fueling Process (Overflowing the Tank) - During the refueling process, overflowing the tank can lead to inaccurate readings. Excess fuel that spills over may not be accounted for in the recorded data, leading to discrepancies.
Note! When refilling for a full tank, it is recommended to conclude the fueling process once the pump automatically shuts off.
Read more about how to effectively manage fleet fuel data here
What to do if the fuel-ups do not match?
If you find that the fuel-ups do not match, it's important to address this issue to ensure accurate tracking of fuel consumption. Regardless of the fuel data source, there are steps that can be taken to improve the readings.
To initiate the resolution process, please reach out to our client support team by sending an email to support@mapon.com
In the email, please include the following information:- Vehicle number whose refueling does not match the actual one;
- Dates showing the error;
- Attach the receipt for the actual refueling as well as receipts for at least 3 previous refuelings in the same vehicle.
This data will be very important for our team to analyze the data thoroughly and apply any necessary corrections to address the discrepancies.